Welcome to JHD Nutrasource!
Shop
Showing 19–27 of 40 results
-

Vitamin a Palmitate 1.7miu
Vitamin A Palmitate (1.7 MIU/g) is a fat-soluble form of Vitamin A, also known as retinyl palmitate. It is a yellow oily liquid or solid at room temperature, with an activity of 1.7 million International Units (IU) per gram。This compound is stable in fats and oils and is often used in various applications due to its beneficial properties.
-
vitamin b1 thiamine hcl
Thiamine HCl (Vitamin B1) is a water-soluble vitamin essential for various bodily functions. It is commonly used to prevent or treat vitamin B1 deficiency.
-

Vitamin B12 1% Cyanocobalamin
Vitamin B12 1% Cyanocobalamin is a synthetic form of vitamin B12 used primarily to treat and prevent vitamin B12 deficiencies. It contains a cyanide group within its molecular structure, which makes it a stable and widely used form of the vitamin. Cyanocobalamin is available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
-
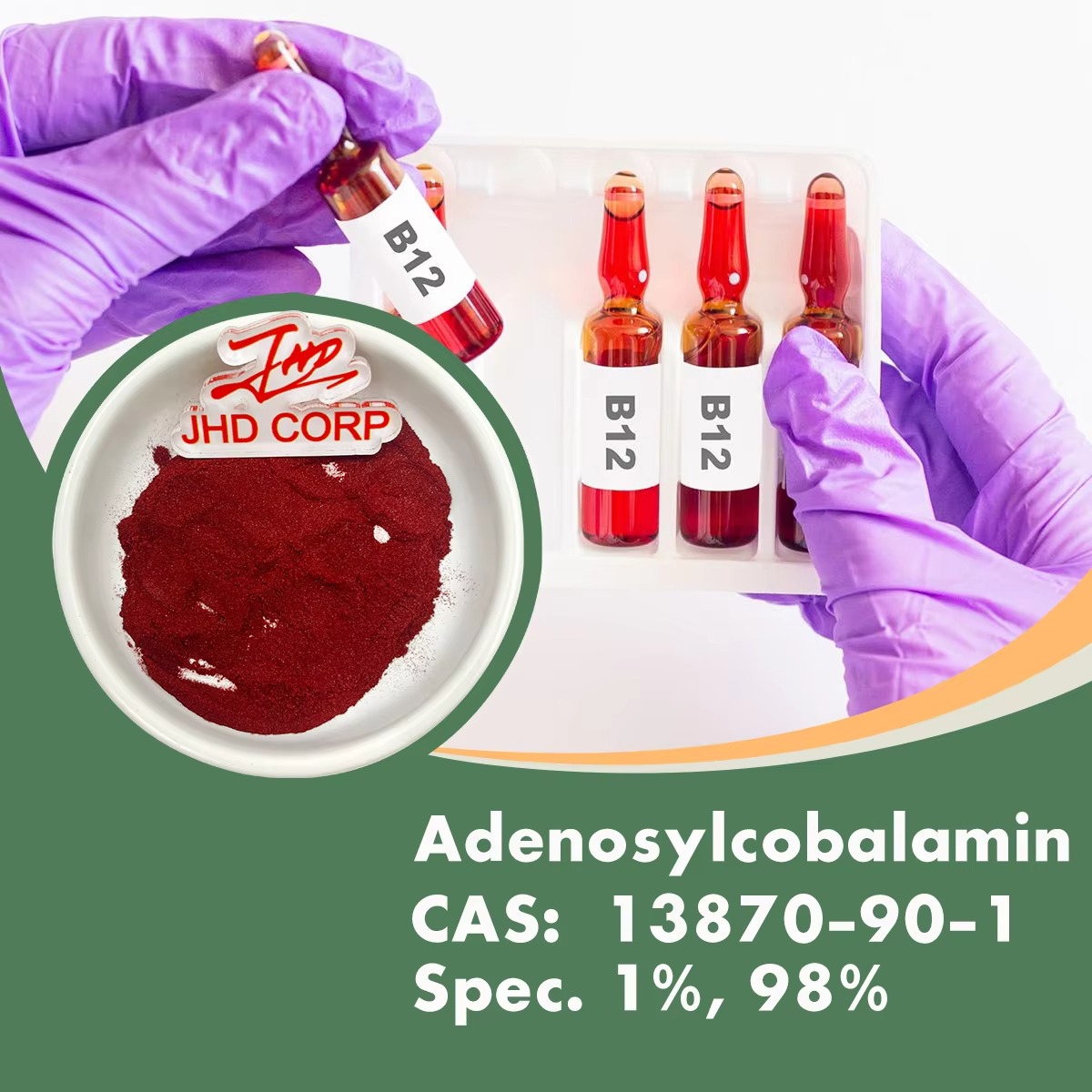
Vitamin B12 Adenosylcobalamin
<strong><b>Short Description</b></strong> Adenosylcobalamin is one of the active forms of vitamin B12. It plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes.
-

Vitamin B12 Methylcobalamin
Methylcobalamin is an active form of Vitamin B12 that is essential for various biological processes. It is particularly important for neurological function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation. Unlike other forms of Vitamin B12, methylcobalamin is directly utilized by the body without the need for conversion.
-

Vitamin B12 Powder
Vitamin B12 Powder, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for human health. It is naturally found in animal-derived foods such as meat, fish, dairy products, and eggs. Vitamin B12 is unique among vitamins because it contains the mineral cobalt and is the only vitamin that is red in color.
-

Vitamin B13 orotic acid
Vitamin B13, also known as orotic acid, is a compound that was historically considered part of the vitamin B complex but is not a true vitamin. It is a precursor in the biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides and RNA. It is found in foods such as organ meats, vegetables like carrots and beets, milk, and dairy products.
-

Vitamin B13 Orotic Acid Powder
<strong>Short Description</strong> Orotic acid, also known as vitamin B13, is a heterocyclic compound and a carboxylic acid. It was historically considered part of the vitamin B complex, but it is now known that it is not a vitamin. It is synthesized in the body via a mitochondrial enzyme, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, or a cytoplasmic enzyme of the pyrimidine synthesis pathway.
-

Vitamin B2
Vitamin B2, also known as riboflavin, is a water - soluble vitamin. It has a yellow - orange color and is relatively stable in dry conditions. However, it can be easily destroyed by light, especially ultraviolet light. Riboflavin is found in a variety of foods. Good food sources include milk and dairy products, eggs, green leafy vegetables, and whole grains. It is also available as a dietary supplement.
